Industry Applications & Pump Solutions
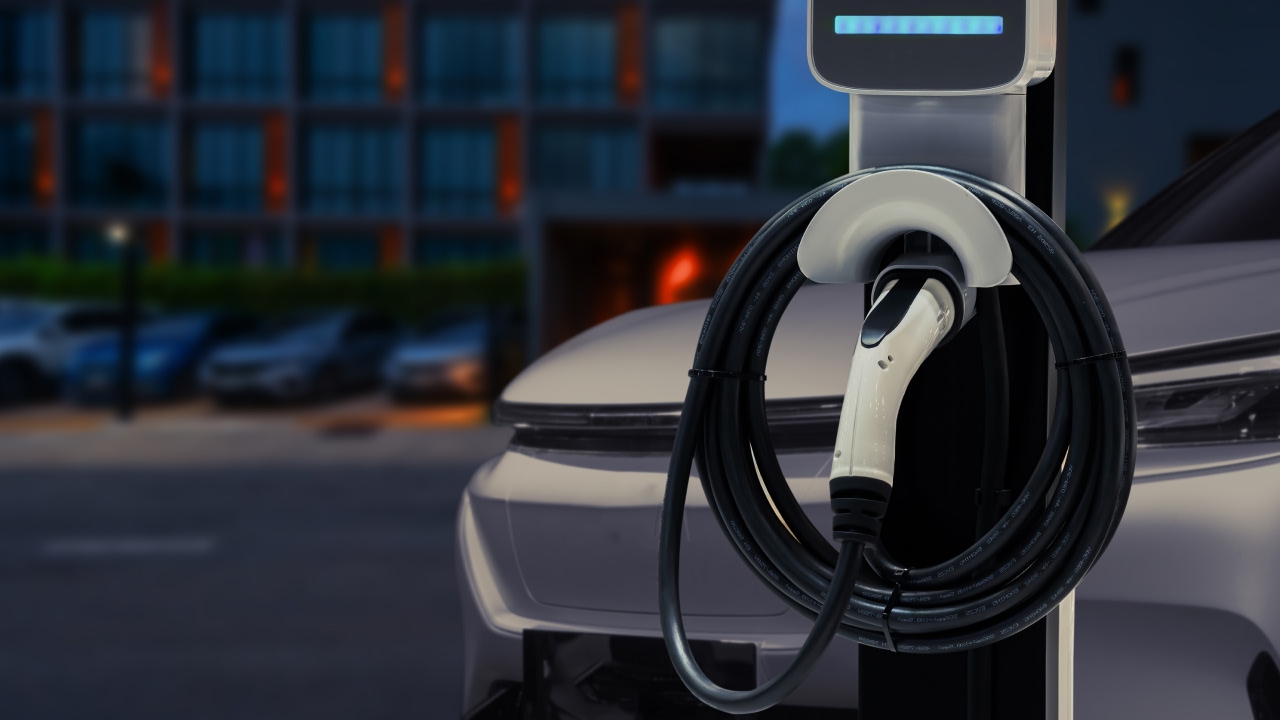

EV Testing Pumps | High Viscosity & Extreme Temperature Solutions for Battery Thermal
EV battery thermal testing requires pumps that handle extreme temperature cycling and viscosity changes. Learn how gear pumps solve seal failure, flow instability, and noise issues in test equipment.

High Temperature Pump Solutions
High Temperature Pump Solutions for Thermal Fluid CirculationAulank provides specialized pumping solutions designed for heat transfer fluids and high-temperature process circulation loops. Targeting media such as Thermal Oil (Heat Transfer Fluid), Superheated Water, and Molten Salts, our pumps are engineered to operate continuously at temperatures ranging from 180°C to over 400°C. By employing unique thermal management structures, we solve common issues like seal failure and bearing seizure caused by extreme heat.Pump Types & Working PrinciplesAir-Cooled High Temperature PumpWorking Principle: Utilizes a physical thermal barrier chamber and cooling fins between the pump casing and the motor. A shaft-mounted fan dissipates heat
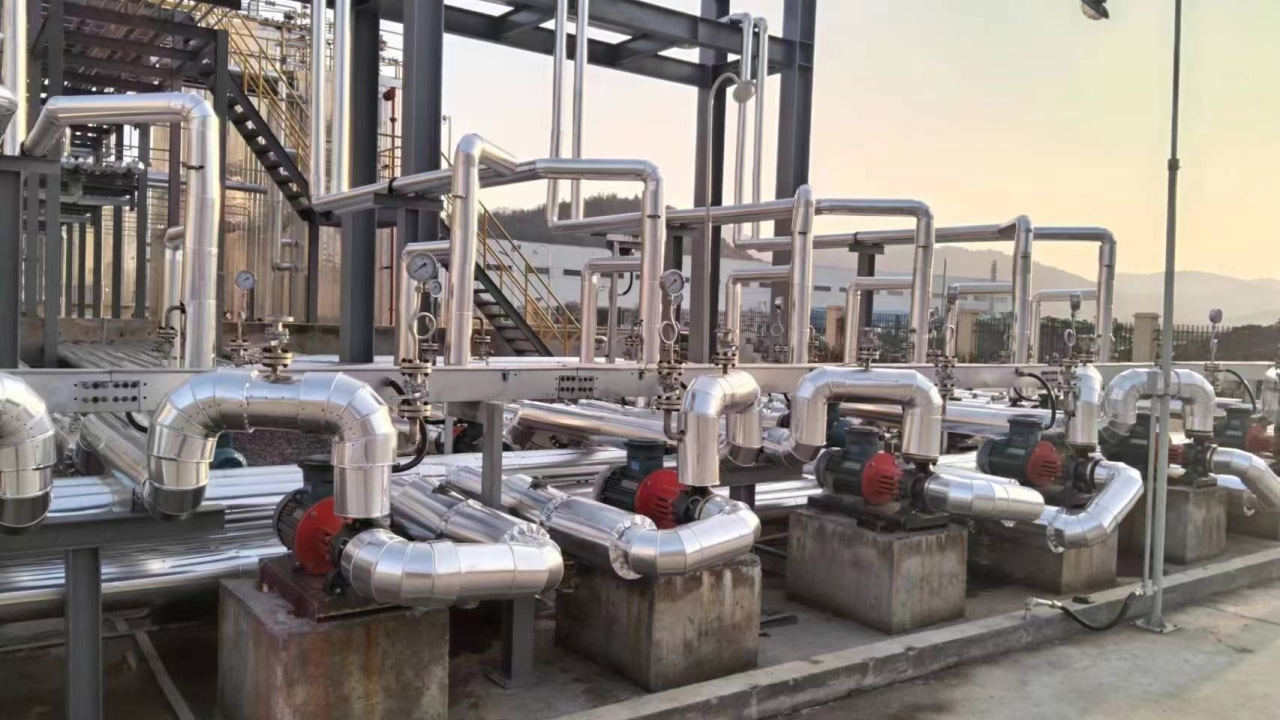

Corrosion Resistant Pump Solutions
Corrosion Resistant Pump Solutions for Aggressive ChemicalsAulank provides specialized pumping solutions designed to withstand the attack of strong acids, alkalis, and aggressive chemical solvents. Targeting fluids such as Sulfuric Acid, Hydrochloric Acid, Nitric Acid, Hydrofluoric Acid, and various organic solvents, our pumps are engineered to prevent material degradation. By utilizing advanced inert materials and specialized structures, we ensure process continuity where standard metal pumps would fail rapidly.Pump Types & Working PrinciplesMagnetic Drive Pump (Sealless Design)Working Principle: This pump operates on the principle of magnetic coupling. The motor drives an outer magnetic rotor, and the magnetic field penetrates a non-metallic isolation
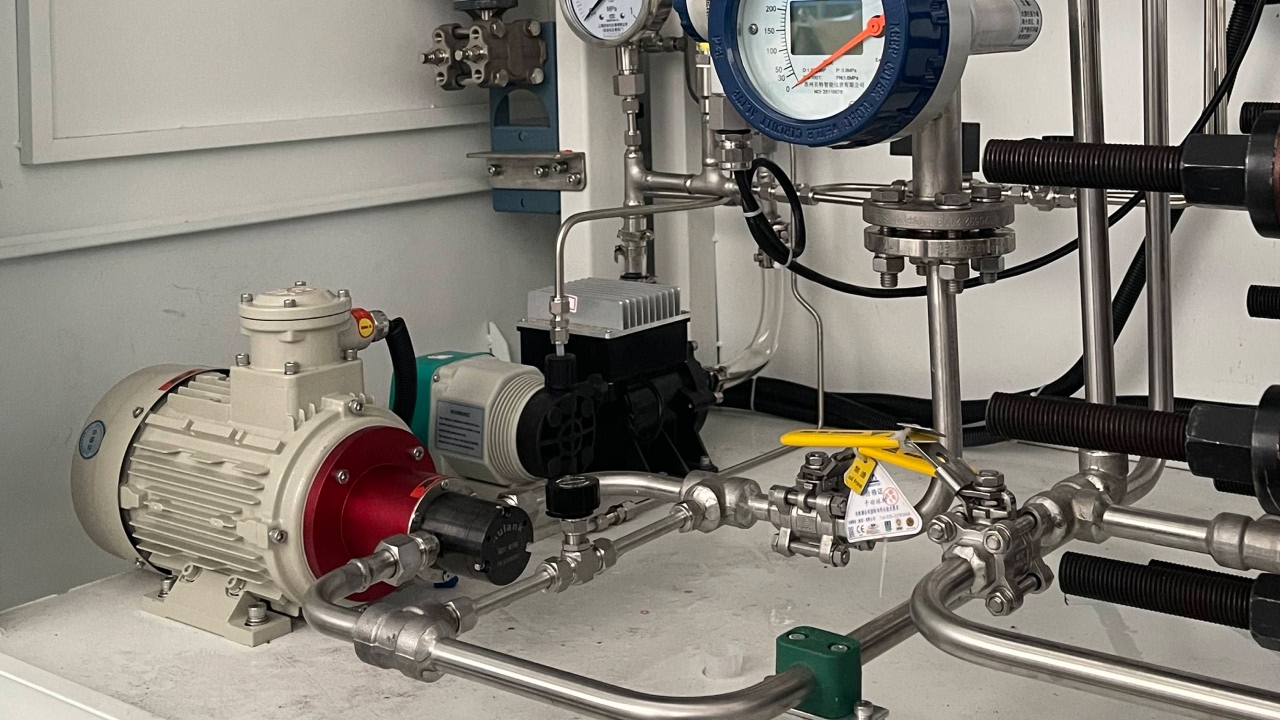

Leak Proof Pump Solutions
Leak Proof Pump Solutions for Hazardous & Volatile FluidsAulank provides leak-proof pump solutions designed for the safe transfer of fluids where any leakage is unacceptable. Targeting strong acids, alkalis, toxic solvents, flammable/explosive liquids, and high-purity media, our solutions utilize sealless technology (Magnetic Drive or Canned Motor) to replace dynamic mechanical seals with static containment shells. This design completely eliminates the risks of fugitive emissions.Key Features of Leak Proof PumpsZero Leakage Design: By eliminating the drive shaft seal—the primary leak path in standard pumps—fluid is hermetically contained within the pump housing, ensuring 100% leak-free operation.Superior Safety: Specifically engineered to handle aggressive
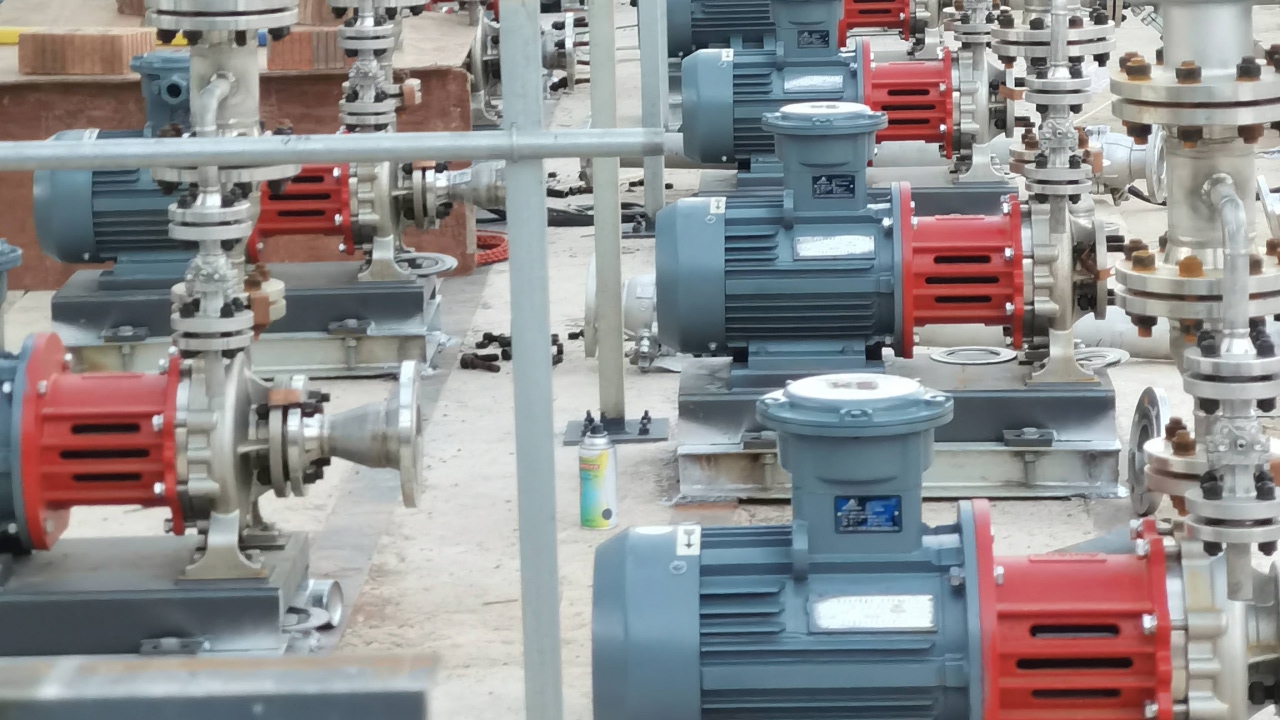

High Viscosity Pump Solutions
High Viscosity Pump Solutions for Thick & Complex FluidsAulank offers solutions for high-viscosity liquid transfer pumps. Fluids such as paints, syrups, coatings, chemical resins, and emulsions possess poor flow characteristics and high internal resistance. Our solutions utilize positive displacement technology to ensure stable, non-pulsating flow, preventing issues like shear thinning, product degradation, or flow stagnation common in standard centrifugal applications.Working Principle & Pump TypesPositive Displacement PrincipleUnlike centrifugal pumps that rely on velocity, high viscosity pumps operate on the positive displacement (PD) principle. They trap a fixed amount of fluid in a cavity and mechanically force it through the discharge. Crucially,
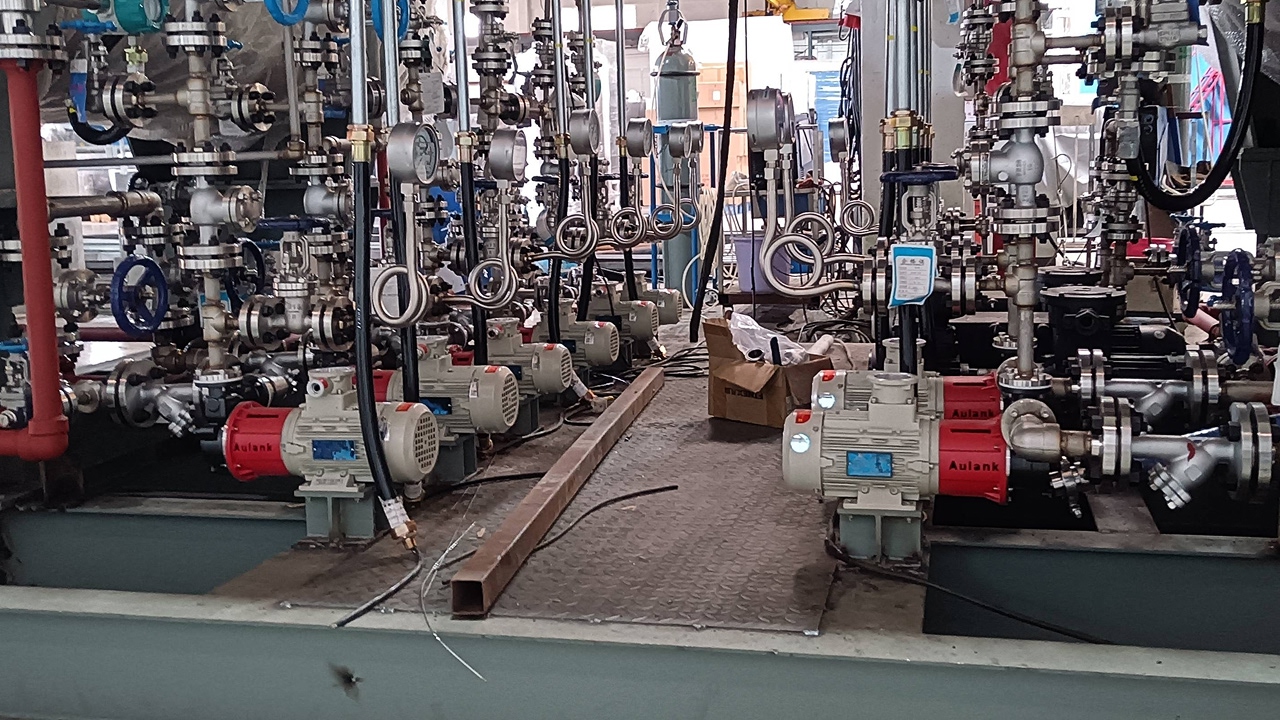

High Flow Rate Pump Solutions
High Flow Rate Pump Solutions for Rapid Volume TransferAulank provides high flow rate pump solutions designed to move massive volumes of water or fluid within a short timeframe. Compared to standard pumps, these units are engineered with larger discharge diameters and optimized hydraulic profiles to prioritize volume throughput over high pressure. They are the critical backbone for applications requiring rapid filling, emptying, or circulation.Working Principle & Pump TypesCentrifugal Operating PrincipleHigh flow pumps primarily operate based on the centrifugal principle. Driven by a motor, the impeller rotates at high speed, creating a vacuum at the center (eye) to suck water in.
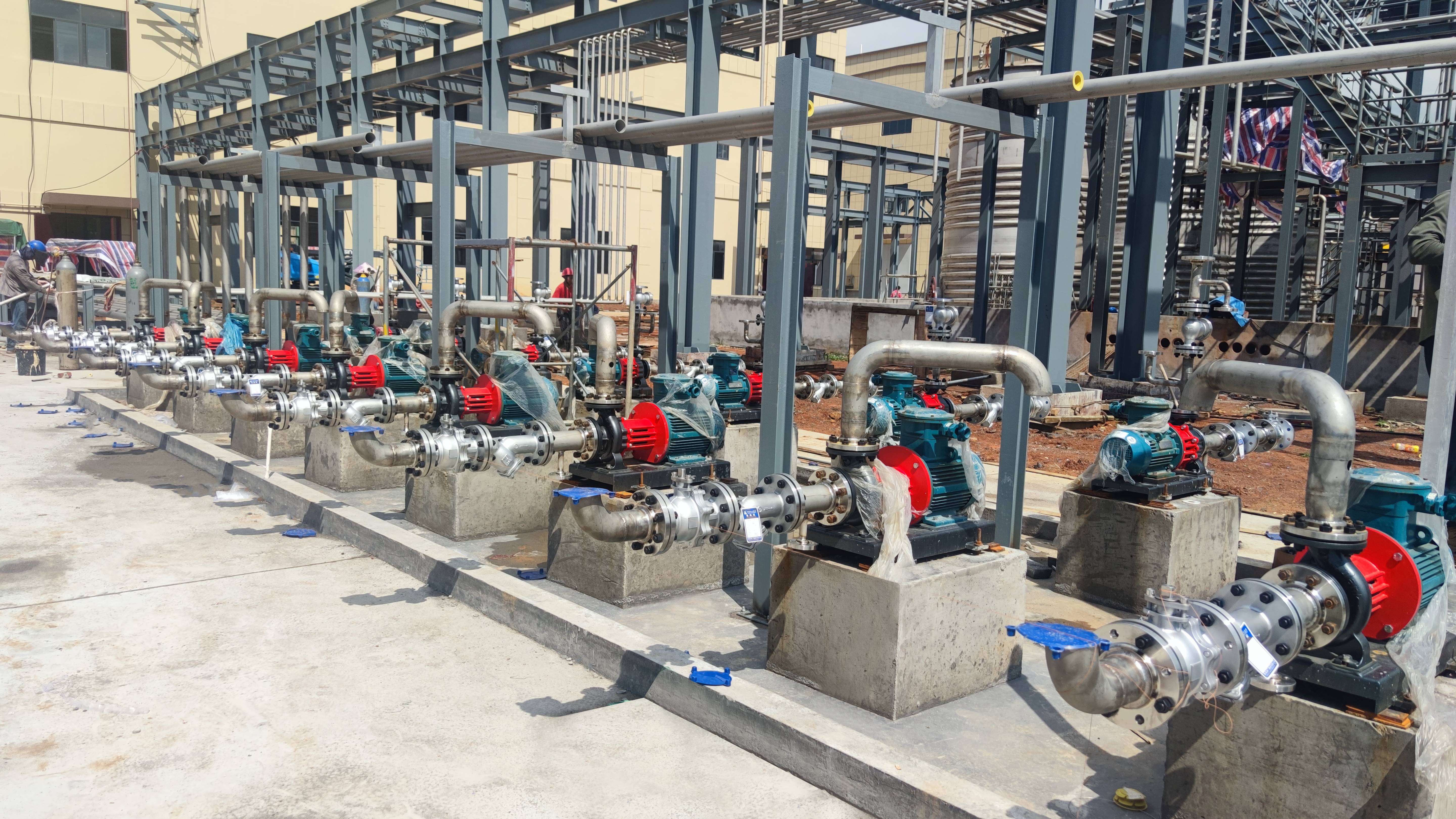

High Head Pump Solutions
High Head Pump Solutions for Long-Distance & Vertical TransferAulank provides specialized high head pump solutions designed to meet the demands of transporting fluids over long distances or overcoming significant vertical elevation changes. Unlike standard pumps that prioritize flow volume, high head pumps are engineered to deliver fluids at high pressure, typically utilizing enclosed impeller designs and robust casings.Key Characteristics of High Head PumpsHigh head pumps are defined by their ability to withstand high internal pressures and rigorous operating conditions.Structural Integrity: Engineered with reinforced materials to handle the stress of high discharge pressures.Impeller Design: Often feature enclosed impellers with tight clearances
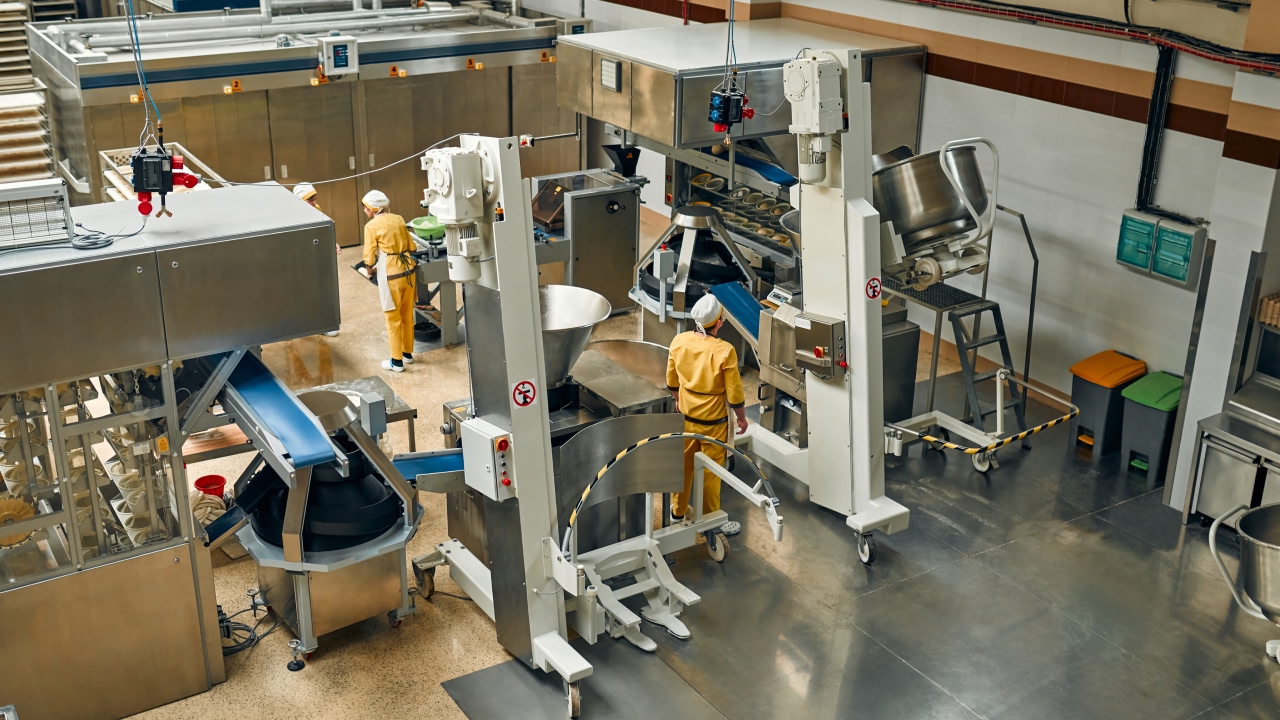

Food Pump Solutions
Food Industry Pump Solutions for Hygienic ProcessingAulank provides the food and beverage industry with professional delivery solutions for liquids, semi-solids, and solids-containing fluids. These solutions strictly adhere to international hygiene standards and regulations such as FDA (21 CFR), EHEDG, and 3-A, and support efficient in-situ cleaning (CIP) and in-situ sterilization (SIP) processes on production lines.Typical Food Industry ApplicationsFood industry pump applications range from raw material transfer to the precise dosing of flavorings and additives. Common scenarios include the transfer of viscous products like syrups and pastes, and the gentle handling of shear-sensitive mixtures. These applications demand pumps that not only
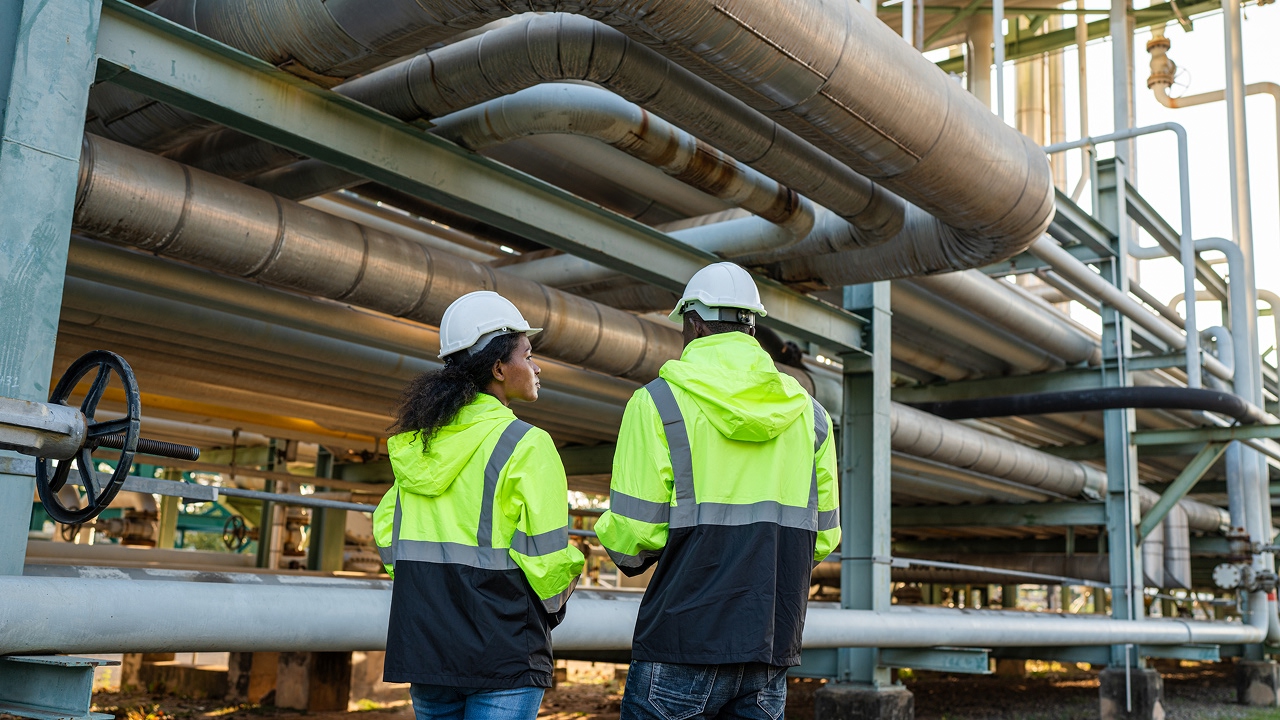

High Pressure Chemical Pump Solutions
High Pressure Chemical Pump Solutions for Process SystemsAulank provides high pressure chemical pump solutions for process systems used in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, new energy, thermal management, and related industrial applications. These solutions are developed based on media characteristics, operating pressure, temperature range, and system configuration. We support pump type selection, parameter matching, material compatibility, and structural configuration, with optional customization and ongoing technical support throughout the operation stage.Typical High Pressure Chemical ApplicationsHigh pressure chemical pump applications are commonly found in continuous chemical transfer, high-pressure circulation systems, metering processes, and sealed chemical handling. These systems place higher demands on pressure stability,

Common Industrial Pump Issues & Solution Approaches
In industrial pump operation, many failures develop gradually rather than occurring suddenly. Early warning signs are often overlooked, or inspection and maintenance are not conducted systematically. The following issues and approaches help clarify root causes, response strategies, and prevention methods.
Key Factors in Industrial Pump Solutions
Common Industrial Pump Issues & Solution Approaches
In industrial pump operation, many failures develop gradually rather than occurring suddenly. Early warning signs are often overlooked, or inspection and maintenance are not conducted systematically. The following issues and approaches help clarify root causes, response strategies, and prevention methods.

Leakage (Seal-Related)
Leakage assessment should begin with identifying leakage location and media condition. Flange or interface leakage is often related to installation stress, misalignment, gasket selection, or tightening torque. Seal leakage requires verification of media temperature, pressure fluctuations, and the presence of dry running, cavitation, or solid particles. Solutions should define seal types and required auxiliary system conditions, such as cooling, flushing, or insulation, and include alignment verification during installation.

Insufficient or Unstable Flow / Head
The primary distinction is whether the issue originates from system resistance changes or deviation from the designed operating point. Filter blockage, valve position changes, air locking, and increased media viscosity can shift the operating point. Entrained gas significantly affects centrifugal and vortex pump performance. Solutions should define normal and extreme operating points and provide selection margins for gas content, temperature variation, and viscosity changes.

Cavitation, Abnormal Noise, and Vibration
Common causes include insufficient NPSH, improper inlet piping design, entrained gas, and vibration amplification caused by installation foundations or piping stress. Diagnosis should begin with inlet conditions—liquid level, pipe diameter, elbows, valves, and strainers—followed by installation and support checks, and finally pump type and speed evaluation. Solutions should specify inlet condition requirements, minimum NPSH margin, and inlet piping constraints.

Accelerated Wear & Abnormal Service Life
Particles, crystallization, contaminants, or improper material matching accelerate wear of wetted parts and sliding components. Thermal cycling further amplifies clearance variation and material fatigue. Evaluation should confirm media cleanliness, crystallization potential, solid content, and compatibility of materials and structural design. Solutions should define filtration requirements, allowable solid content, and critical material combinations.

Excessive Temperature Rise & Efficiency Loss
This typically occurs when pumps operate for extended periods outside optimal efficiency ranges due to system resistance changes or insufficient heat dissipation, especially in compact installations or high ambient temperature environments. Assessment should return to operating point verification and performance curves, combined with checks of cooling, insulation, and installation space. Solutions should define allowable temperature rise, ambient temperature limits, and installation space constraints during selection.
FAQs
How do we select the most suitable industrial pump for our operating conditions?
Which operating condition data must be clearly defined during pump selection?
Can rated pump parameters be used directly for selection?
What should be prioritized for high- or low-temperature applications?
Do gas-containing or micro-flow applications require special pump design?
When should customized industrial pump solutions be considered?
What are common selection mistakes during system integration?
How can proper selection reduce long-term operational risk?
Are industrial pump solutions only relevant for large-scale projects?